Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-06-06 Origin: Site








Choosing the right Power Cable is critical to ensuring electrical safety, device efficiency, and compliance with regulations. With various types, ratings, and applications available, many people often ask, “How do I know what power cable to use?” In this in-depth guide, we’ll explore the factors that determine power cable selection, provide data-driven comparisons, analyze current trends in cable technology, and answer common questions—all while optimizing for the search term Power Cable and related keywords.
Before diving into specifics, it’s essential to understand what a Power Cable actually is. A power cable is an assembly of conductors used to transmit electrical power. It typically includes a conductor (such as copper or aluminum), insulation, and a protective outer sheath. The selection of a Power Cable depends on several critical factors including:
Voltage rating
Current carrying capacity (ampacity)
Application environment (indoor/outdoor, wet/dry)
Conductor material
Length of the cable run
Safety and regulatory requirements
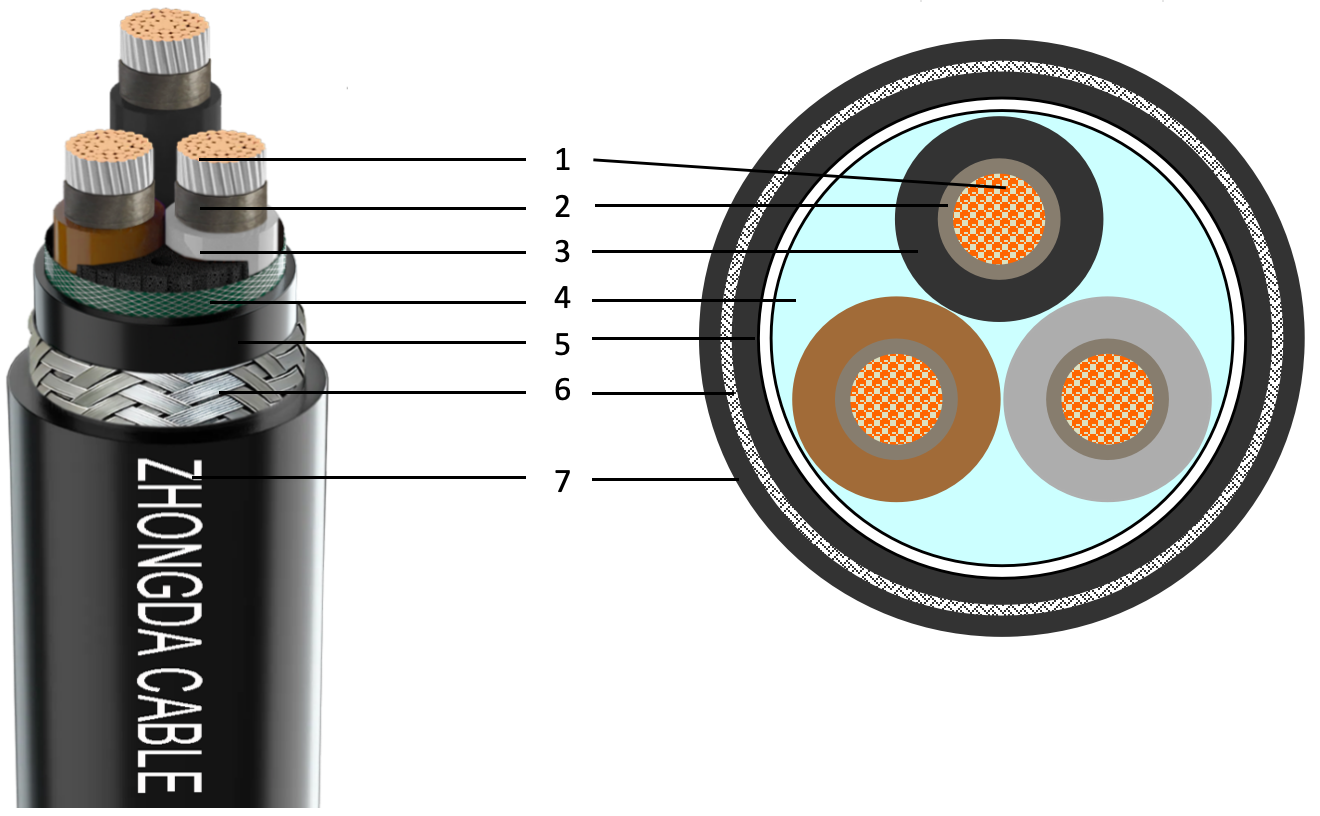
The most common types of Power Cables include:
| Power Cable Type | Application | Voltage Rating | Insulation Type | Environment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flexible Power Cable | Temporary power supply for tools and equipment | Up to 600V | PVC or Rubber | Indoor, outdoor |
| Armoured Cable (SWA) | Underground or harsh environment use | 600V to 1,000V | XLPE, Steel Wire Armour | Underground, industrial |
| Coaxial Cable | Signal transmission (TV, internet) | Low voltage | PVC or PE | Indoor |
| Submersible Cable | Pumps and underwater motors | Up to 1,000V | Rubber or PE | Wet, submersed areas |
| High Voltage Power Cable | Industrial grids and power transmission | Above 1,000V | XLPE | Outdoor, industrial |
Choosing the right type depends heavily on the installation environment and the operational requirements.
Every Power Cable has a specific voltage rating. You must choose a cable that matches or exceeds the operating voltage of your device or system. Using an under-rated cable can result in insulation breakdown or even fire.
Power Cables are rated by the amount of current (in amperes) they can carry without overheating. Refer to manufacturer datasheets or industry standard ampacity tables to determine the appropriate size. Here’s a simplified table:
| Cable Size (mm²) | Current Rating (Amps) | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|
| 1.5 | 14 – 20 A | Lighting circuits |
| 2.5 | 20 – 25 A | Socket outlets |
| 6.0 | 32 – 40 A | Air conditioners, small heaters |
| 10.0 | 45 – 60 A | Electric cookers, industrial machinery |
| 16.0+ | 60 – 100+ A | Main supply, heavy equipment |
Long cable runs can result in voltage drop, which affects the performance of electrical equipment. To minimize voltage drop:
Choose a thicker conductor
Use a cable rated for higher ampacity
Keep cable runs as short as possible
The operating environment plays a significant role in Power Cable selection. Consider the following:
Indoor vs. Outdoor: Outdoor-rated cables are UV and moisture resistant.
Temperature: High-temperature areas need heat-resistant insulation like XLPE.
Chemical Exposure: Industrial settings may require cables with chemical-resistant sheaths.
Flexibility: For movable equipment, Flexible Power Cables are ideal.
Most Power Cables are made of either copper or aluminum. Copper has better conductivity but is heavier and more expensive. Aluminum is cheaper and lighter but requires a larger size for the same conductivity.
Ensure your chosen Power Cable complies with local and international standards such as:
UL (Underwriters Laboratories)
IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission)
RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances)
ISO (International Standards Organization)
These certifications ensure safety, reliability, and environmental sustainability.
With the growing adoption of renewable energy, electric vehicles, and smart home systems, Power Cable requirements are evolving. Here are some modern trends:
Smart Power Cables now come with embedded sensors that monitor temperature, voltage, and current in real time. These are particularly useful in industrial automation and IoT-enabled systems.
In sensitive areas like hospitals and data centers, low-smoke zero halogen (LSZH) cables are preferred. These emit minimal toxic fumes during a fire.
Solar Power Cables and wind turbine cables are designed to withstand UV radiation, wide temperature ranges, and high mechanical stress.
Manufacturers are increasingly using recyclable materials and adopting green manufacturing practices in Power Cable production.
Here’s a comparison chart for quick decision-making:
| Application | Recommended Power Cable | Key Feature | Why It’s Best |
|---|---|---|---|
| Home appliances | Flexible Power Cable | Ease of movement, bend radius | Safe for dynamic usage |
| Underground wiring | Armoured Cable (SWA) | Steel wire armor for protection | Resists mechanical stress |
| Electric vehicle charger | High Voltage Cable | High insulation and ampacity | Handles fast charging needs |
| Solar panel connection | Solar Power Cable | UV-resistant and weatherproof | Ensures outdoor durability |
| Data centers | Halogen-Free Cable | Fire-retardant and low smoke emission | Meets stringent fire safety codes |
A power cable refers to the internal or external wire system used for permanent electrical installations, whereas a power cord is typically a detachable cable used to connect appliances to outlets.
No. Using an incorrect Power Cable can result in damage, overheating, or even electrical fires. Always check voltage, current rating, and connector compatibility.
You need to consider the current draw of the device, the length of the cable, and acceptable voltage drop. Use an ampacity calculator or consult an electrician.
Armoured Power Cables with weatherproof sheaths are ideal for outdoor applications. They resist UV, moisture, and mechanical impact.
Not necessarily. Thicker cables carry more current but are more expensive and harder to handle. Choose based on the specific load and distance requirements.
Look for UL, IEC, RoHS, or CE certifications, depending on your location and the application to ensure quality and safety compliance.
Choosing the correct Power Cable involves evaluating multiple factors, from voltage and current to environmental conditions and regulations. With modern advancements in cable technology, understanding your specific needs is crucial to making an informed decision. Whether you're wiring a home, setting up industrial machinery, or connecting solar panels, selecting the right Power Cable ensures performance, safety, and long-term reliability.
By applying the insights and comparison data in this guide, you can confidently determine what Power Cable to use for any situation. Always refer to manufacturer datasheets and consult professionals when in doubt—your safety depends on it.
